
Evaporators are crucial components in refrigeration systems, responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding space or substance to be cooled, thereby causing the refrigerant to evaporate and change from a liquid to a vapor state. They come in various types and play a vital role in both Freon and ammonia-based refrigeration systems. Here are the details:
Evaporators:
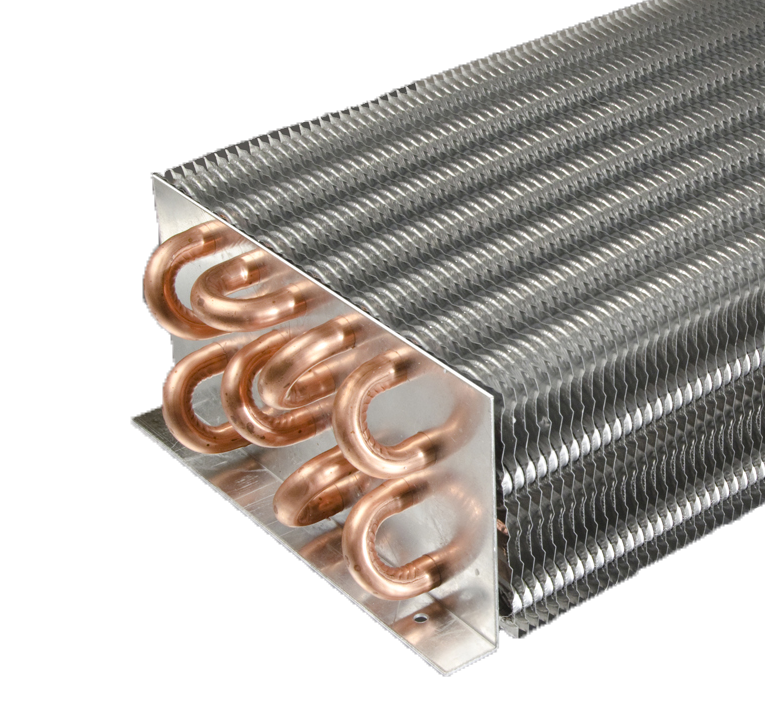
- Types of Evaporators:
- Fin and Tube Evaporators: Consist of a network of tubes through which the refrigerant flows, surrounded by fins to increase the surface area for heat transfer.
- Plate Evaporators: Utilize a series of plates with channels for the refrigerant flow, providing efficient heat exchange in a compact design.
- Shell and Tube Evaporators: Comprise a shell housing multiple tubes through which the refrigerant passes, with water or another fluid flowing around the tubes for heat exchange.
- Immersion Evaporators: Directly immerse the refrigerant-carrying components into the substance to be cooled, facilitating rapid heat transfer.
- Working Principle:
- The low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant enters the evaporator and absorbs heat from the surrounding space or substance.
- As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it evaporates, changing from a liquid to a vapor state.
- The evaporation process causes a cooling effect, lowering the temperature of the substance being cooled.
- The refrigerant vapor exits the evaporator and is drawn into the compressor to begin the refrigeration cycle anew.
- Components:
- Coils or Tubes: Provide a surface for heat exchange between the refrigerant and the substance being cooled.
- Expansion Device: Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, controlling the rate of evaporation and ensuring proper cooling.
- Fans (for air-cooled evaporators): Circulate air over the evaporator coils, enhancing heat transfer and cooling efficiency.
- Defrosting Mechanism: Prevents the buildup of frost or ice on the evaporator coils, ensuring optimal performance.
- Advantages:
- Evaporators are essential for removing heat from the space or substance being cooled, allowing for effective temperature control.
- They are available in various configurations to suit different refrigeration applications, from small-scale residential units to large industrial systems.
- Evaporators facilitate energy-efficient cooling by utilizing the latent heat of vaporization of the refrigerant.
- They play a critical role in maintaining product quality and freshness in refrigerated storage and transportation applications.

Application in Freon and Ammonia Systems:
Evaporators are integral components of both Freon and ammonia refrigeration systems, functioning similarly in each type of system to facilitate heat transfer and cooling. The choice between Freon and ammonia systems depends on factors such as the desired temperature range, environmental considerations, and specific application requirements.
Before selecting an evaporator for a refrigeration system, several factors should be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here are key considerations:
- Refrigerant Type:
- The choice of evaporator should be compatible with the refrigerant used in the system (e.g., Freon or ammonia).
- Consider the thermodynamic properties, operating pressures, and safety considerations associated with the refrigerant.
- Application Requirements:
- Determine the cooling capacity and temperature range required for the specific application.
- Consider factors such as space constraints, installation location, and environmental conditions (e.g., ambient temperature and humidity).
- Type of Refrigeration System:
- The type of refrigeration system (e.g., vapor compression, absorption) will influence the selection of the evaporator design and configuration.
- Consider whether the system is used for air conditioning, refrigerated storage, process cooling, or other applications.
- Heat Load and Heat Transfer Requirements:
- Evaluate the heat load to be removed by the evaporator and the required heat transfer rate.
- Consider factors such as the heat exchange surface area, airflow (for air-cooled evaporators), and fluid flow rates (for liquid-cooled evaporators).
- Operating Conditions:
- Consider the operating conditions, including ambient temperature, humidity levels, and operating pressures, to ensure the evaporator can perform effectively under all conditions.
- Evaluate any potential variations in load or operating parameters to select an evaporator capable of handling fluctuations.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Assess the energy efficiency of the evaporator design, considering factors such as heat transfer efficiency, pressure drop, and fan power consumption (for air-cooled evaporators).
- Select an evaporator that offers high efficiency to minimize energy consumption and operating costs.
- Material Compatibility and Corrosion Resistance:
- Ensure that the materials used in the construction of the evaporator are compatible with the refrigerant and operating conditions.
- Consider corrosion resistance, especially in applications where corrosive substances are present or in harsh environments.
- Maintenance and Serviceability:
- Evaluate the ease of maintenance and serviceability of the evaporator, considering factors such as access to components, cleaning requirements, and availability of spare parts.
- Choose an evaporator design that facilitates routine maintenance and minimizes downtime.
- Regulatory and Safety Requirements:
- Ensure compliance with relevant regulatory standards and safety requirements for the specific application and operating environment.
- Consider any safety features or certifications required for the evaporator, especially in applications involving hazardous materials or environments.
- Cost and Lifecycle Considerations:
- Assess the initial cost, installation expenses, and long-term lifecycle costs associated with the evaporator.
- Consider factors such as durability, reliability, and expected lifespan to determine the overall cost-effectiveness of the evaporator solution.
Several reputable brands specialize in manufacturing evaporators and other refrigeration components. Here are some well-known brands that are recognized for their quality, reliability, and innovative technology:
- Danfoss: Danfoss is a global leader in refrigeration and air conditioning solutions, offering a wide range of evaporators suitable for various applications. Their products are known for their energy efficiency, durability, and advanced control features.
- Alfa Laval: Alfa Laval is a trusted provider of heat transfer solutions, including evaporators for refrigeration systems. They offer a diverse portfolio of evaporator designs, ranging from plate heat exchangers to shell and tube configurations, known for their efficiency and reliability.
- Tecumseh: Tecumseh is a leading manufacturer of compressors and refrigeration components, including evaporators. Their evaporator products are designed for commercial refrigeration applications and are valued for their performance, durability, and ease of installation.
- Heatcraft Refrigeration Products: Heatcraft is a division of Lennox International and specializes in commercial refrigeration solutions. They offer a comprehensive range of evaporators, including air-cooled and water-cooled models, known for their quality construction and efficient performance.
- Colmac Coil Manufacturing: Colmac Coil is a reputable manufacturer of custom heat exchangers, including evaporators for refrigeration applications. They specialize in innovative designs tailored to specific customer requirements, with a focus on energy efficiency and durability.
- Frascold: Frascold is a renowned manufacturer of refrigeration compressors and components, including evaporators. Their evaporator products are known for their high-quality construction, reliability, and efficient heat transfer capabilities.
- Evapco: Evapco specializes in cooling and refrigeration solutions, offering a range of evaporators for industrial and commercial applications. Their evaporator products are designed for optimal performance, durability, and ease of maintenance.
- Kelvion: Kelvion (formerly known as GEA Heat Exchangers) is a global provider of heat transfer solutions, including evaporators for refrigeration systems. They offer a wide range of evaporator designs tailored to various applications, known for their efficiency and reliability.
- Lu-Ve Group: Lu-Ve is an Italian manufacturer of heat exchangers and refrigeration components, including evaporators. Their evaporator products are known for their quality construction, energy efficiency, and innovative design features.
- Baltimore Aircoil Company (BAC): BAC specializes in evaporative cooling solutions, offering evaporators for both air conditioning and refrigeration applications. Their evaporator products are recognized for their energy efficiency, reliability, and sustainable design.
When selecting a brand, it’s essential to consider factors such as product reliability, performance, customer support, and compatibility with your specific application requirements. Additionally, consulting with industry experts and reviewing customer feedback can help ensure you choose a reputable brand that meets your needs effectively.
Evaporators can get damaged due to various reasons, ranging from improper installation and maintenance practices to external factors and system-related issues. Here are some common reasons why evaporators may get damaged:
- Corrosion: Corrosion of evaporator coils can occur due to exposure to corrosive substances, such as acids or chemicals present in the air or the substances being cooled. Corrosion weakens the coil material, leading to leaks and reduced efficiency.
- Frost or Ice Buildup: If the defrosting system fails to operate correctly or is not sized adequately for the application, frost or ice can accumulate on the evaporator coils. Excessive frost buildup can impair heat transfer efficiency and cause damage to the coils over time.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect installation of the evaporator, such as inadequate support or improper refrigerant line connections, can lead to stress on the coils or damage to other components, resulting in leaks or reduced performance.
- Poor Maintenance: Lack of regular maintenance, such as failure to clean the evaporator coils or replace air filters, can lead to reduced airflow, increased pressure drop, and potential damage to the coils due to dirt or debris buildup.
- Refrigerant Leakage: Evaporator coils can develop leaks due to corrosion, physical damage, or faulty welds. Refrigerant leakage not only leads to reduced cooling capacity but can also cause damage to the surrounding components and pose safety hazards.
- Overheating: Inadequate airflow or refrigerant flow over the evaporator coils can cause them to overheat, leading to thermal stress and potential damage. This can occur due to factors such as clogged air filters, malfunctioning fans, or improper refrigerant charge.
- Freezing of Liquid Refrigerant: If liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator coils instead of vapor, it can cause the coils to freeze and expand, leading to mechanical damage, including coil rupture or tube deformation.
- Vibration or Mechanical Stress: Excessive vibration or mechanical stress on the evaporator coils, such as from nearby machinery or improper mounting, can lead to fatigue failure or structural damage over time.
- Chemical Contamination: Exposure to chemical contaminants, such as cleaning agents or refrigerant additives, can degrade the coil material and cause corrosion or other forms of chemical damage.
- Environmental Factors: External factors such as exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or environmental pollutants can contribute to the degradation of evaporator coils over time.
To prevent evaporator damage, it’s essential to follow proper installation procedures, conduct regular maintenance, ensure correct sizing and operation of the defrosting system, and monitor for signs of corrosion or other potential issues. Additionally, addressing any system-related issues promptly and using high-quality materials and components can help extend the lifespan and reliability of evaporators.
Installing an evaporator correctly is crucial to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity of the refrigeration system. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind during the installation process:
- Location and Mounting:
- Choose a location for the evaporator that allows for adequate airflow and accessibility for maintenance.
- Ensure proper clearance around the unit to facilitate airflow and heat dissipation.
- Mount the evaporator securely on a stable surface to minimize vibration and ensure proper alignment with the refrigerant lines.
- Refrigerant Line Connections:
- Properly connect the refrigerant lines to the evaporator, ensuring tight seals and leak-free joints.
- Use appropriate fittings and connections compatible with the refrigerant type and operating pressures.
- Follow manufacturer’s recommendations for brazing or soldering techniques to ensure strong, reliable connections.
- Electrical Connections:
- Connect electrical wiring to the evaporator components, such as fans and defrost heaters, following the manufacturer’s wiring diagram and electrical codes.
- Ensure proper grounding of the unit to prevent electrical hazards and ensure safe operation.
- Condensate Drainage:
- Install a condensate drain pan beneath the evaporator to collect and remove condensate water.
- Ensure the drain pan slopes toward the drain outlet and is properly connected to a suitable drainage system to prevent water buildup and potential leaks.
- Defrost System Installation:
- If the evaporator is equipped with a defrosting system, ensure proper installation of defrost heaters, temperature sensors, and controls.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for configuring and testing the defrost cycle to ensure effective removal of frost or ice buildup on the coils.
- Airflow Considerations:
- Verify proper airflow direction and orientation of the evaporator unit according to the installation manual.
- Ensure that airflow is not obstructed by nearby objects or obstructions and that there is adequate space for air circulation around the unit.
- Insulation and Vapor Barrier:
- Install insulation around the refrigerant lines and components to prevent condensation and heat loss.
- Use vapor barriers to protect insulation from moisture infiltration and ensure its effectiveness over time.
- Pressure Testing and Leak Detection:
- Perform a pressure test on the refrigerant lines and evaporator coils to verify system integrity and detect any leaks.
- Use appropriate leak detection methods, such as soap bubbles or electronic leak detectors, to identify and address any leaks promptly.
- Commissioning and Testing:
- Once installed, commission the evaporator unit by verifying proper operation of all components, including fans, defrost system, and temperature controls.
- Monitor system performance and temperature distribution to ensure consistent cooling and proper function of the evaporator.
- Documentation and Compliance:
- Keep detailed records of the installation process, including equipment specifications, installation diagrams, and test results.
- Ensure compliance with local building codes, regulations, and industry standards for refrigeration system installation and operation.
By following these considerations and guidelines during the installation of an evaporator, you can help ensure the proper functioning, efficiency, and reliability of the refrigeration system for its intended application.
The evaporator is a crucial component in the refrigeration cycle, responsible for absorbing heat from the space or substance being cooled, thereby causing the refrigerant to evaporate and change from a liquid to a vapor state. The specifications and components of an evaporator may vary depending on the specific application and refrigeration system type. Below are the key components and specifications commonly associated with evaporators, along with the refrigeration cycle they belong to:
Components of an Evaporator:
- Coils or Tubes: Provide a surface area for heat exchange between the refrigerant and the substance being cooled. They are typically made of copper, aluminum, or stainless steel.
- Expansion Device: Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, controlling the rate of evaporation and ensuring proper cooling. Common types include thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs) and capillary tubes.
- Fans (for Air-Cooled Evaporators): Circulate air over the evaporator coils to enhance heat transfer and cooling efficiency. They may be axial or centrifugal fans depending on the application.
- Defrosting Mechanism: Prevents the buildup of frost or ice on the evaporator coils, ensuring optimal performance. Defrosting methods include electric heaters, hot gas injection, water sprays, or off-cycle defrosting.
- Drain Pan: Collects condensate water that forms during the cooling process and channels it to a drain outlet to prevent water buildup and potential leaks.
Specifications of an Evaporator:
- Cooling Capacity: The amount of heat absorbed by the evaporator per unit time, typically measured in kilowatts (kW) or British thermal units per hour (BTU/hr).
- Coil Surface Area: The total surface area of the evaporator coils or tubes, which determines the heat transfer efficiency and cooling capacity.
- Refrigerant Flow Rate: The rate at which refrigerant flows through the evaporator coils, controlled by the expansion device and measured in pounds per hour (lb/hr) or kilograms per hour (kg/hr).
- Operating Temperature Range: The range of temperatures over which the evaporator can effectively cool the substance being cooled, specified in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F).
- Refrigerant Compatibility: The type of refrigerant compatible with the evaporator, determined by factors such as operating pressures, temperature range, and material compatibility.
- Pressure Drop: The pressure loss across the evaporator coils, which affects the system’s overall efficiency and performance.
Refrigeration Cycle: The evaporator is part of the vapor compression refrigeration cycle, which includes four main components: compressor, condenser, expansion device, and evaporator. In this cycle, the evaporator is where the low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant absorbs heat from the space or substance being cooled, causing it to evaporate and change phase from a liquid to a vapor. The refrigerant vapor is then compressed by the compressor and condensed in the condenser before returning to the evaporator to complete the cycle.
Immenso.com.bd stands as a beacon of reliability and trustworthiness in the realm of refrigeration solutions. Renowned for its unwavering commitment to excellence, Immenso.com.bd has earned its place as a distinguished supplier of top-tier evaporators. With a steadfast dedication to quality, this esteemed entity prides itself on offering a comprehensive selection of evaporators sourced exclusively from reputable and renowned brands.
Immenso.com.bd boasts an extensive portfolio of evaporators, each meticulously curated to meet the highest standards of performance, efficiency, and durability. From cutting-edge designs to proven reliability, every evaporator showcased by Immenso.com.bd reflects a commitment to excellence that transcends expectations.
As a purveyor of premium refrigeration components, Immenso.com.bd understands the importance of reliability and integrity. With a reputation built upon years of exemplary service and unparalleled customer satisfaction, Immenso.com.bd stands as a trusted partner for businesses seeking superior evaporator solutions.
Whether it’s for commercial, industrial, or residential applications, Immenso.com.bd delivers unparalleled expertise and unwavering dedication to customer satisfaction. With a team of seasoned professionals at the helm, Immenso.com.bd ensures a seamless procurement experience, backed by unparalleled support and guidance every step of the way.
In a world where quality reigns supreme, Immenso.com.bd stands as a beacon of excellence, offering a gateway to premium evaporators that redefine industry standards. For those in search of reliability, performance, and peace of mind, Immenso.com.bd emerges as the ultimate destination for all evaporator needs.


